Parkinsons disease is a progressive disease with selective dopaminergic neuronal loss. Parkinsons disease is the second cause of progressive chronic neurodegenerative disease it has a high prevalence and incidence generates a high impact on the quality of life of patients and significant costs due to its healthcare.
The mechanisms of cell death are based upon oxidative stress and apoptosis.

Parkinson disease pathophysiology pdf. The effects of dopamine loss are eventually widespread and account for the varied symptoms experienced by those with PD. Dopamine is a neurotransmitter that. Parkinsons disease many atypical variants sometimes called Parkinsons Plus Syndromes and any other brain disease that resembles Parkinsons such as normal pressure hydrocephalus vascular parkinsonism or drug-induced parkinsonism.
The behavior of neurons in the basal ganglia is severely disrupted in Parkinsons disease PD. Because of its rhythmic nature and. Degradation of dopaminergic pathways specifically in the.
In nonhuman parkinsonian primate models the disturbance in neurons in basal ganglia output structures include increased firing bursting an augmented synchrony correlated activity and a tendency towards loss of specificity in their receptive fields. Parkinsons disease is developed due to the degeneration of dopaminergic neurons in the substance nigra pars compacta which is manifested in the appearance of motor. The pathophysiology is at present better understood with plurifactorial etiology including genetic predisposition and environmental toxic factors.
These were explored in terms of pathophysiology and imaging as well as in-depth discussion of the. Pathophysiology of Parkinsons Disease Parkinsons disease is chronic disorder of the nervous system. So what exactly is Parkinsons disease PD.
PD is a type of movement disorder that can affect the ability to perform common daily activities. Although significant progress has been made in our understanding of the clinical deficits of PD the detailed pathophysiology of PD is still a problem that is not yet solved. Parkinsons disease PD is a progressive neurological disorder characterised by a large number of motor and non-motor features that can impact on function to a variable degree.
Pathology The most prominent pathological findings in Parkinsons disease are degeneration of the darkly pigmented dopamine neurons in the substantia nigra loss of dopamine in the neostriatum and the presence of intracellular inclusion bodies known as Lewy bodies. Other neuronal populations are also affected in Parkinsons disease to a much lesser extent but they may contribute to some of the other pathology. The cells that produce dopamine are damaged in people with Parkinsons disease.
These symptoms are typically divided into those that affect movement motor symptoms and those that do not non-motor. PATHOPHYSIOLOGY OF PARKINSONS DISEASE MICHAEL J. Parkinson disease is a slowly progressive chronic neurological disease that effects a small area of nerve cells in an area of the brain known as the substantia nigra.
Delegates attended a series of lectures by specialists that largely focused on non-dopaminergic dysfunction in PD. The understanding of the pathophysiology of Parkin-sons disease PD is a major precondition for develop-ing new treatment and diagnosis strategies for this com-mon disease. This review describes the clinical characteristics of PD with emphasis on those features that differentiate the disease from other parkinsonian disorders.
Parkinsons disease as a chronic progressive neurodegenerative condition resulting from the loss of the dopamine-containing cells of the substantia nigra. BURKE ParkinsonsdiseasePDisthoughttoaffectmorethan1 millionpeopleintheUnitedStatesalone1ofevery100 individualsabovetheageof55Inthetwocenturiessince itwasfirstdescribedbyJamesParkinsonwehavelearneda. Tau in the Pathophysiology of Parkinsons Disease Lina Pan1 Lanxia Meng1 Mingyang He1 Zhentao Zhang1 Received.
The tremor is also seen during postural action after a short pause and is often called re-emergent tremor although it appears that the physiology is the same. During the pan-European event world-renowned experts in Parkinsons disease PD presented the latest findings in the pathophysiology and management of the disease. Johns Hopkins Medicine based in Baltimore Maryland.
As a manifestation of Parkinsons disease it is separate from bradykinesia and rigidity as the magnitude of tremor is not. 18 September 2020 Accepted. Although PD is associated with a wide range of symptoms there are features of PD that most people with the condition will experience.
It isnt fatal but it can cause debilitating symptoms that impact everyday movement and mobility. 1 The diagram below shows the location of the substantia nigra and the dopamine pathway in the brain. In all cases of parkinsonism there is a disturbance in.
Although loss of dopaminergic neurons occurs with age such cell death is rapidly accelerated in PD. The pathophysiology of Parkinsons Disease is linked to the degradation of dopaminergic neurons in the brain. This cells normally produces dopamine a chemical neurotransmission that transmits signal between areas in the brain that when working normally coordinates smooth and balanced muscle movement.
The heterogeneity of dopaminergic neuronal loss leads to etiopathogenic clues. There are a number of tremors that may affect patients with Parkinsons disease but the classic is tremor-at-rest. This abnormal neuronal behavior transmitted to the.
10 December 2020 The Authors 2021 Abstract The pathological hallmarks of Parkinsons disease PD are the progressive loss of dopaminergic neurons in the substantia.

Pdf Pathogenesis Of Parkinson S Disease Dopamine Vesicles And Alpha Synuclein

Progress Towards Therapies For Disease Modification In Parkinson S Disease The Lancet Neurology
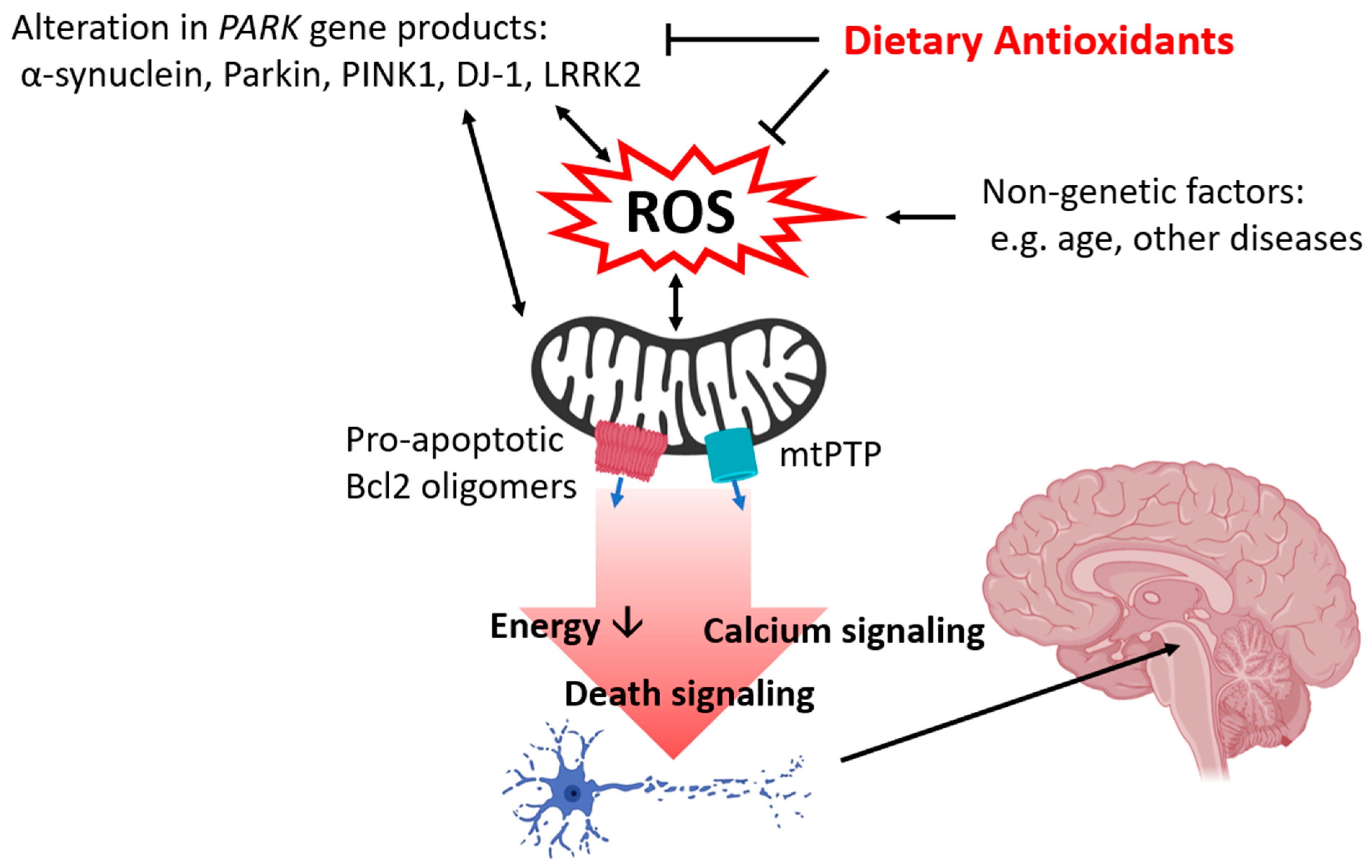
Antioxidants Free Full Text Dietary Antioxidants And Parkinson S Disease Html

Lewy Bodies In Parkinson S Disease Parkinsons Disease Lewy Body Parkinsons Disease Nursing
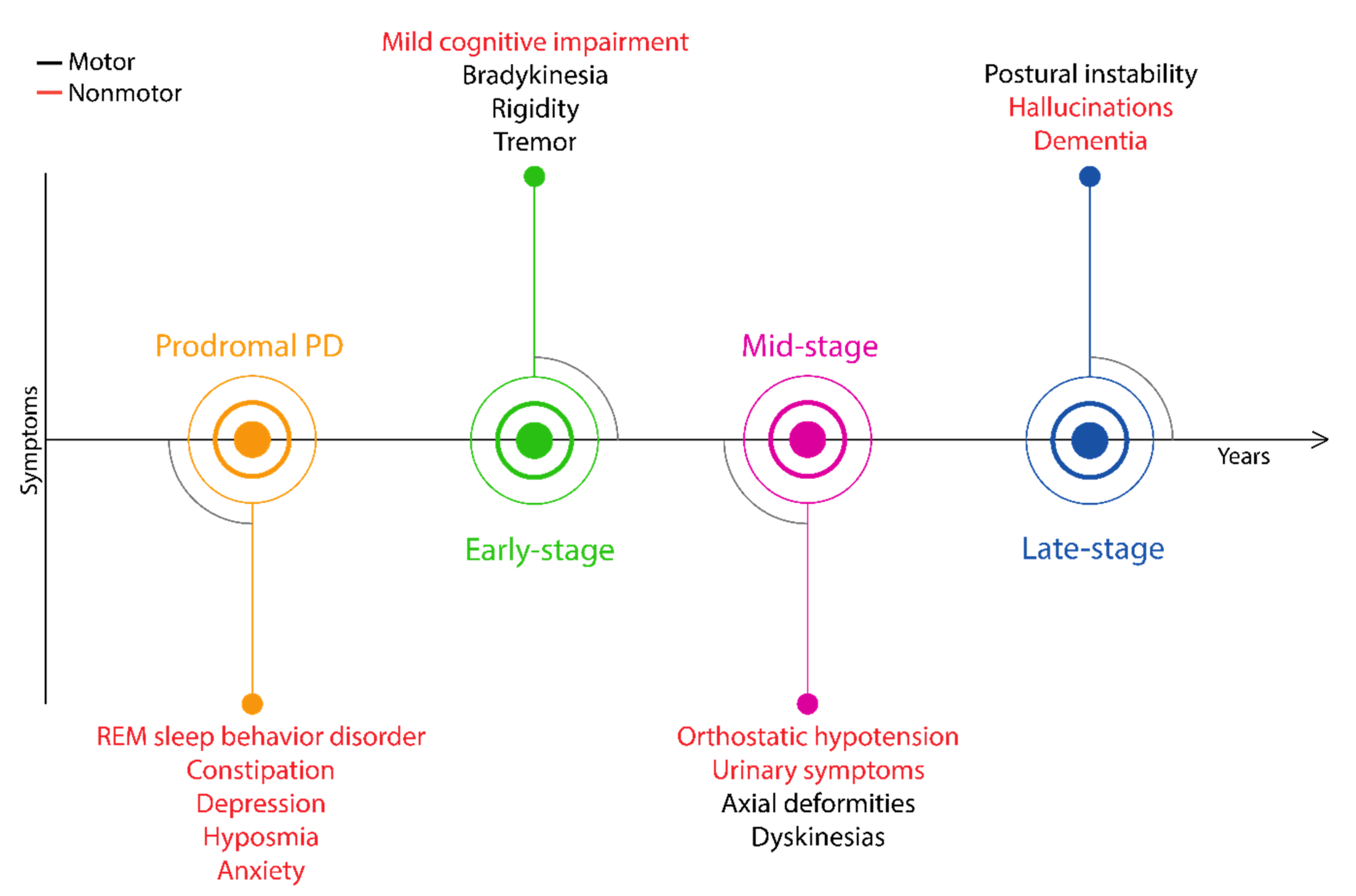
Biology Free Full Text Clinical Features Of Parkinson S Disease The Evolution Of Critical Symptoms Html

Pin On Parkinson S Disease Treatment
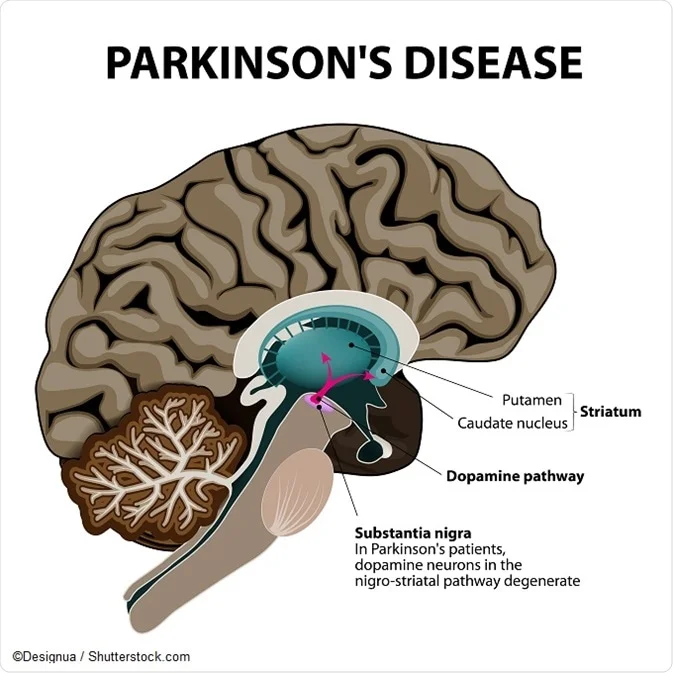
Parkinson S Disease Pathophysiology

Risk Factors For Non Motor Symptoms In Parkinson S Disease The Lancet Neurology
Parkinson S Disease Pathogenesis And Clinical Findings Calgary Guide
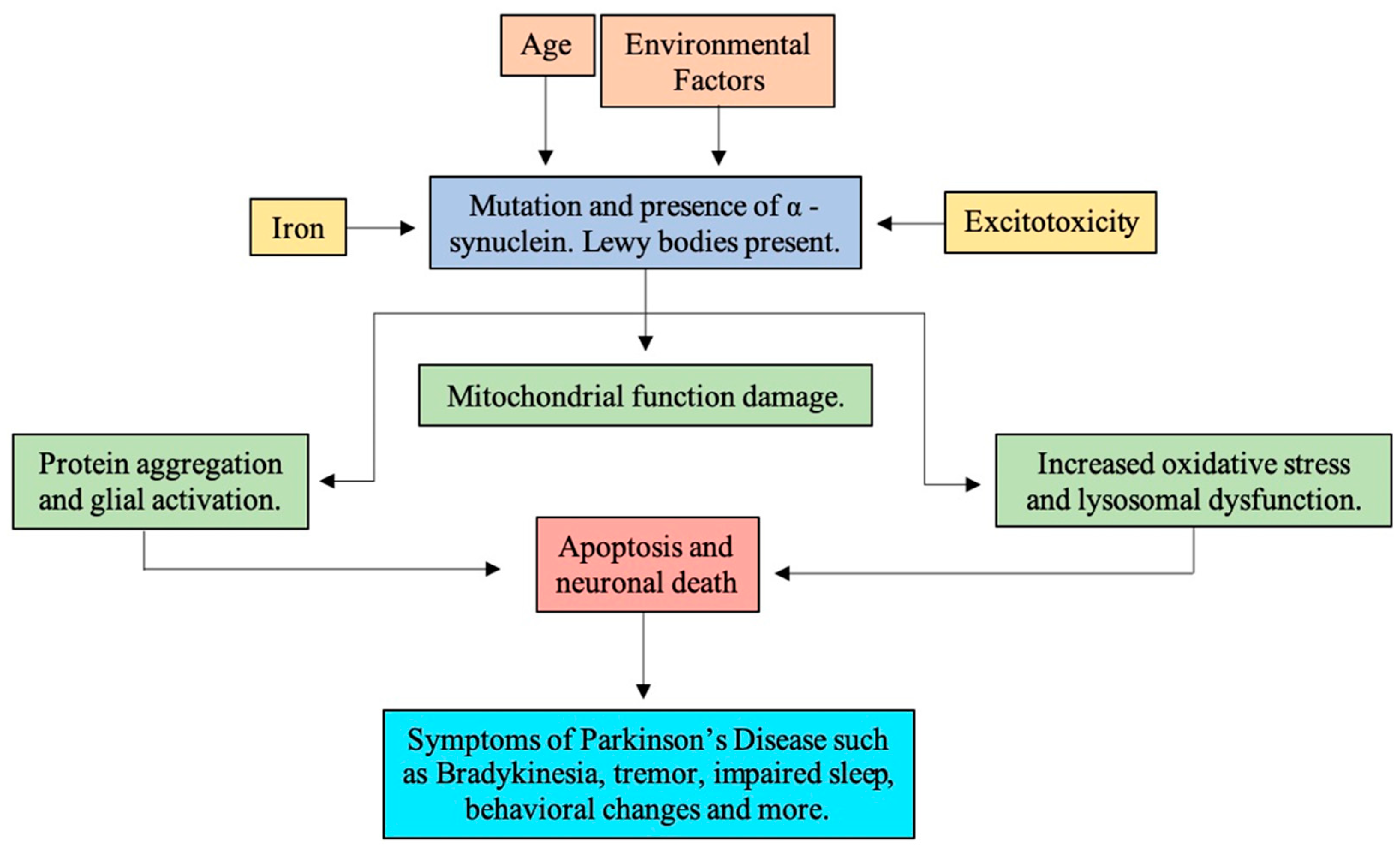
Molecules Free Full Text The Pathology Of Parkinson S Disease And Potential Benefit Of Dietary Polyphenols Html
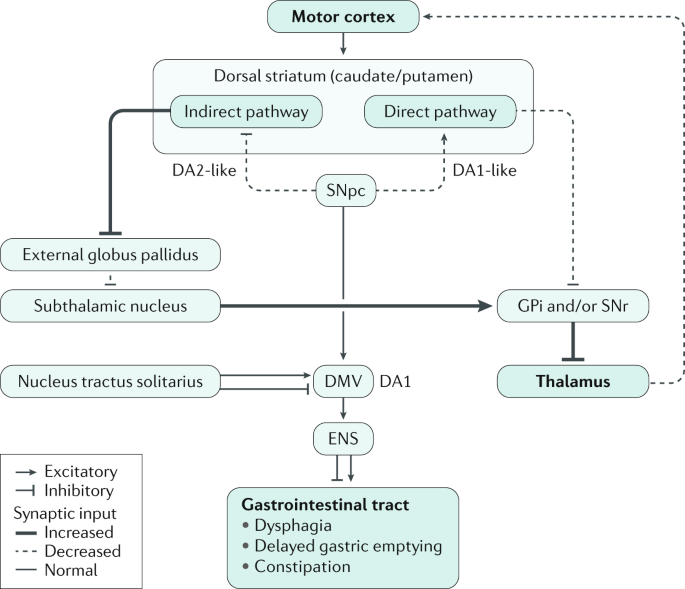
Parkinson Disease And The Gut New Insights Into Pathogenesis And Clinical Relevance Nature Reviews Gastroenterology Hepatology

Pathogenesis Of Parkinson S Disease At Molecular Level Showing Download Scientific Diagram
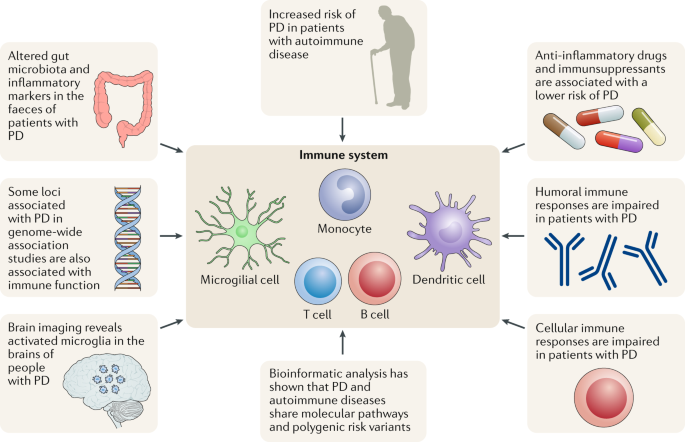
Parkinson Disease And The Immune System Associations Mechanisms And Therapeutics Nature Reviews Neurology

Parkinson Disease American Family Physician

Etiology Of Parkinson S Disease An Overview Sciencedirect Topics
Https Www Hopkinsmedicine Org Neurology Neurosurgery Research Labs Udall Center Docs Pathophysiology Pd Dawson Pdf
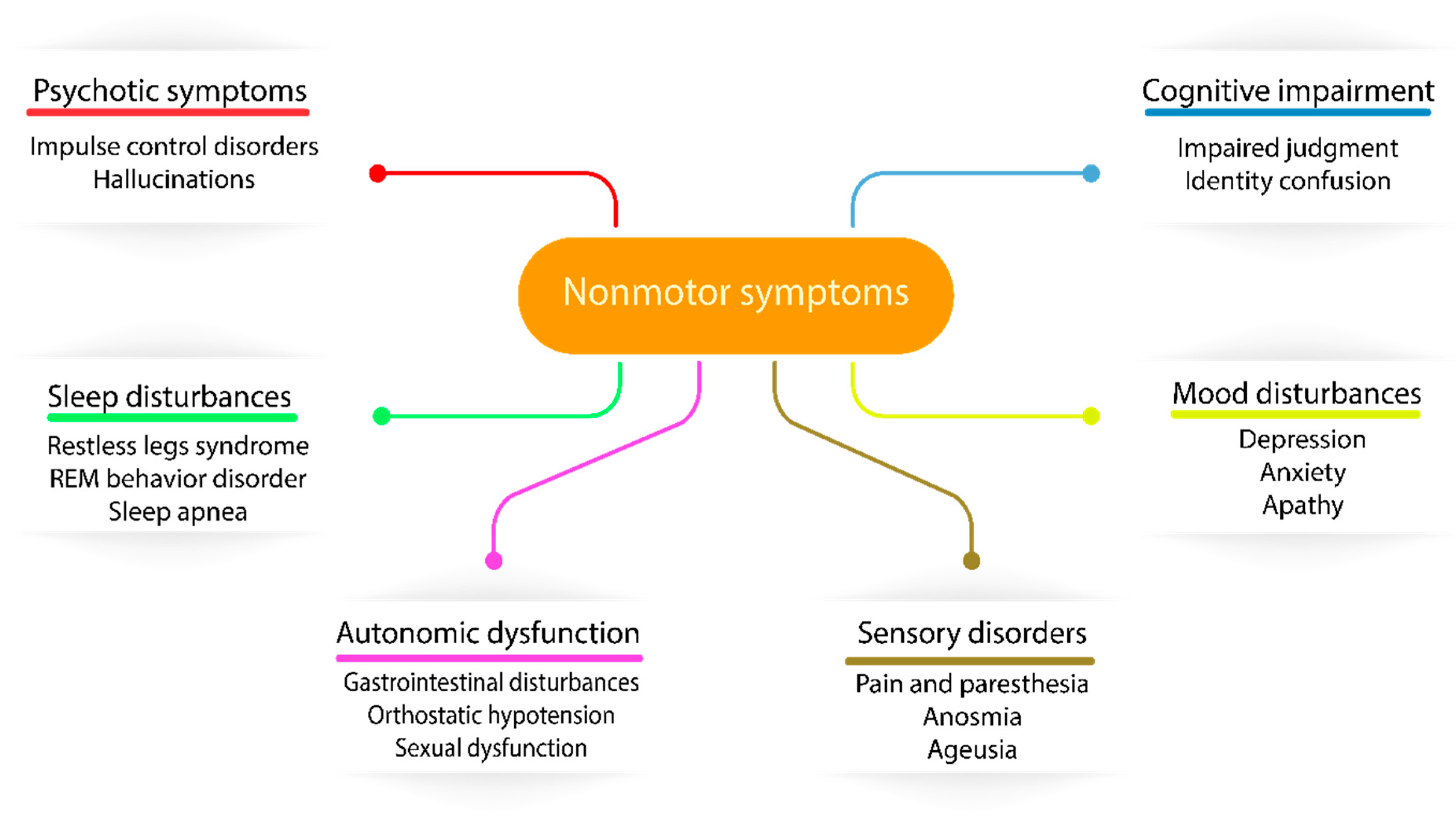
Biology Free Full Text Clinical Features Of Parkinson S Disease The Evolution Of Critical Symptoms Html


